West Bengal Fact file
- West Bengal is situated in eastern India and shares its borders with Jharkhand, Bihar, Orissa, Sikkim and Assam. The state also shares international borders with Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal.
- Bengali is the official language of the state, though English and Hindi are also widely spoken. Nepali is primarily spoken in Darjeeling district.
- Kolkata, Siliguri, Asansol, Durgapur, Raniganj, Kharagpur, Haldia, Darjeeling, Malda, Midnapore, Cooch Behar and Howrah are some of the key cities in the state.
- West Bengal’s climate varies from tropical savannah in the southern portions to humid sub tropical in the north.
Male population (million) = 46.9
Female population (million) = 44.4
Manipur Factfile
Tea, petroleum and petrochemicals, leather. Iron and steel, information technology, mineral resources, automobile and auto components, biotechnology, fisheries, jute products and textiles.
West Bengal is situated in eastern India and shares its borders with Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, Sikkim and Assam. The state also shares international borders with Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal. The Bay of Bengal is in the south of the state.
It is India’s sixth largest economy, and recorded a gross state domestic product (GSDP) of US$ 117.4 billion in 2013-14. The state’s GSDP expanded at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.5 per cent during 2005-14.
West Bengal is the second largest tea-producing state in India. During 2013-14, it accounted for 25.8 per cent of India’s total tea production with production of around 312.1 million kgs. Kolkata is the prime centre for India’s jute industry. During 2012-13, West Bengal accounted for 79.6 per cent of India’s total jute production.
Its locational advantage makes the state a traditional market for eastern India, the Northeast, Nepal and Bhutan. It is also a strategic entry point for markets in Southeast Asia. The cost of operating a business is lower in Kolkata than in other metropolitan cities.
West Bengal has abundant natural resources of minerals and suitable agro-climatic conditions for agriculture, horticulture and fisheries. It is in vicinity to mineral rich states like Jharkhand, Bihar and Odisha. It offers excellent connectivity to the rest of India in terms of railways, roadways, ports and airports.
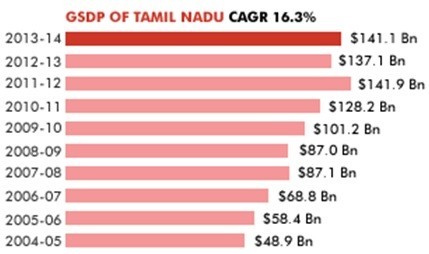
At current prices, Tamil Nadu’s gross state domestic product (GSDP) was about US$ 141.1 billion in 2013-14.
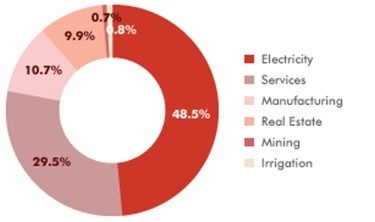
Over 2013-14, outstanding investments in West Bengal totaled US$ 108.4 billion.

